Fire Incident Management Checklist
Master fire incident management with our comprehensive checklist. Ensure swift response, coordination, and safety measures during emergencies with our preplanning resources
Empower your fire department with effective fire hazard mitigation strategies. Enhance safety protocols and readiness to protect communities efficiently.
Published:April 30, 2024
Edited:April 30, 2024

Empower your fire department with effective fire hazard mitigation strategies. Enhance safety protocols and readiness to protect communities efficiently.
Effective fire hazard mitigation is essential for safeguarding lives, property, and the environment from the increasing threat of fires. In recent years, with the heightened frequency and severity of wildfires, the importance of proactive measures to reduce fire risks has become increasingly evident. From identifying potential fire hazards to implementing preventive measures and ensuring prompt response capabilities, successful fire hazard mitigation requires a comprehensive approach that addresses the unique challenges and vulnerabilities of each community in today’s world.
Fire hazard mitigation is a form of community risk reduction (CRR), which involves taking proactive and preventative measures to enhance safety. It involves collaboration among various stakeholders to prevent emergencies, mitigate risks, and prepare for disasters through engagement, prevention measures, and education initiatives. More specifically, hazard mitigation involves identifying potential fire hazards and implementing strategies to prevent fires from starting or spreading.1
Fire hazard mitigation is crucial, particularly in recent years with the increase in wildfires. These events have highlighted the importance of proactive measures to reduce fire risks. Factors such as climate change, land use patterns, and human activities have contributed to the increase in fire frequency and severity.2 Mitigation measures, such as implementing fire-resistant building materials, creating defensible spaces around homes, and establishing wildfire buffer zones, can help reduce the risk of wildfires spreading to communities. Mitigation efforts help protect lives by preventing injuries and fatalities, preserving property from damage or destruction, and safeguarding the environment from the devastating impacts of fires. Fire hazard mitigation efforts also contribute to economic resilience by minimizing the financial losses associated with fire damage, including property loss, business interruption, and healthcare costs.4
Fire hazard mitigation involves several critical steps to effectively reduce the risk and impact of fires. Although the mitigation planning process can look different for each state and or region, there are four core steps to every hazard mitigation plan: Organize the planning process and recourse, assess risks and capabilities, develop a mitigation strategy, and adopt and implement the plan.3 Here is an in-depth breakdown of each step:
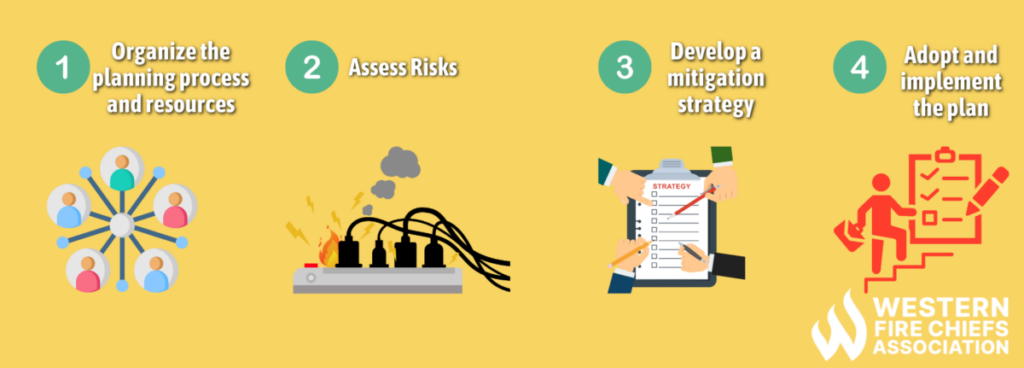
Organize the planning process and resources: This step involves bringing together a team of stakeholders from various sectors, including government agencies, emergency services, community organizations, and residents. The team collaborates to coordinate efforts and resources and establish a structured approach to fire hazard mitigation. Key tasks during this phase include identifying leadership roles, defining objectives and priorities, assessing available resources (such as personnel, funding, and equipment), and establishing communication channels.
Assess risks: Assessing risks in fire hazard mitigation involves identifying potential fire hazards, evaluating their likelihood and potential consequences, and prioritizing mitigation efforts accordingly. This process includes cataloging hazards, considering factors like ignition sources and environmental conditions, and assessing vulnerabilities within the community. Tools like hazard mapping and stakeholder engagement are used to gather insights and develop targeted strategies.
Develop a mitigation strategy: Based on the analysis from the risk assessment, specific actions and measures are outlined to address the identified hazards and vulnerabilities within the community. The mitigation strategy typically includes a combination of preventive measures, such as promoting fire safety education, implementing building codes and regulations, and enhancing emergency response capabilities.5 Stakeholder input and collaboration are essential in developing a strategy that is tailored to the unique needs and challenges of the community. By developing a mitigation strategy, communities can proactively address fire hazards and enhance their resilience to fire emergencies.
Adopt and implement the plan: Adopting and implementing the plan is the final crucial step in fire hazard mitigation. Once the mitigation strategy is developed, it needs to be officially adopted and put into action. This involves gaining approval from relevant authorities and stakeholders, allocating necessary resources, and executing the planned actions. Implementing the plan includes deploying preventive measures such as controlling ignition sources, promoting fire safety practices, and installing detection and suppression systems. Continuous monitoring and evaluation are essential to ensure the effectiveness of the plan and make adjustments as needed.4
Master fire incident management with our comprehensive checklist. Ensure swift response, coordination, and safety measures during emergencies with our preplanning resources
Enhance fire department operations with our comprehensive guide to the Incident Command System (ICS). Streamline coordination for efficient emergency response.
Empower your fire department with effective fire hazard mitigation strategies. Enhance safety protocols and readiness to protect communities efficiently.